20 Oct · Neurotech 101
What is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation?
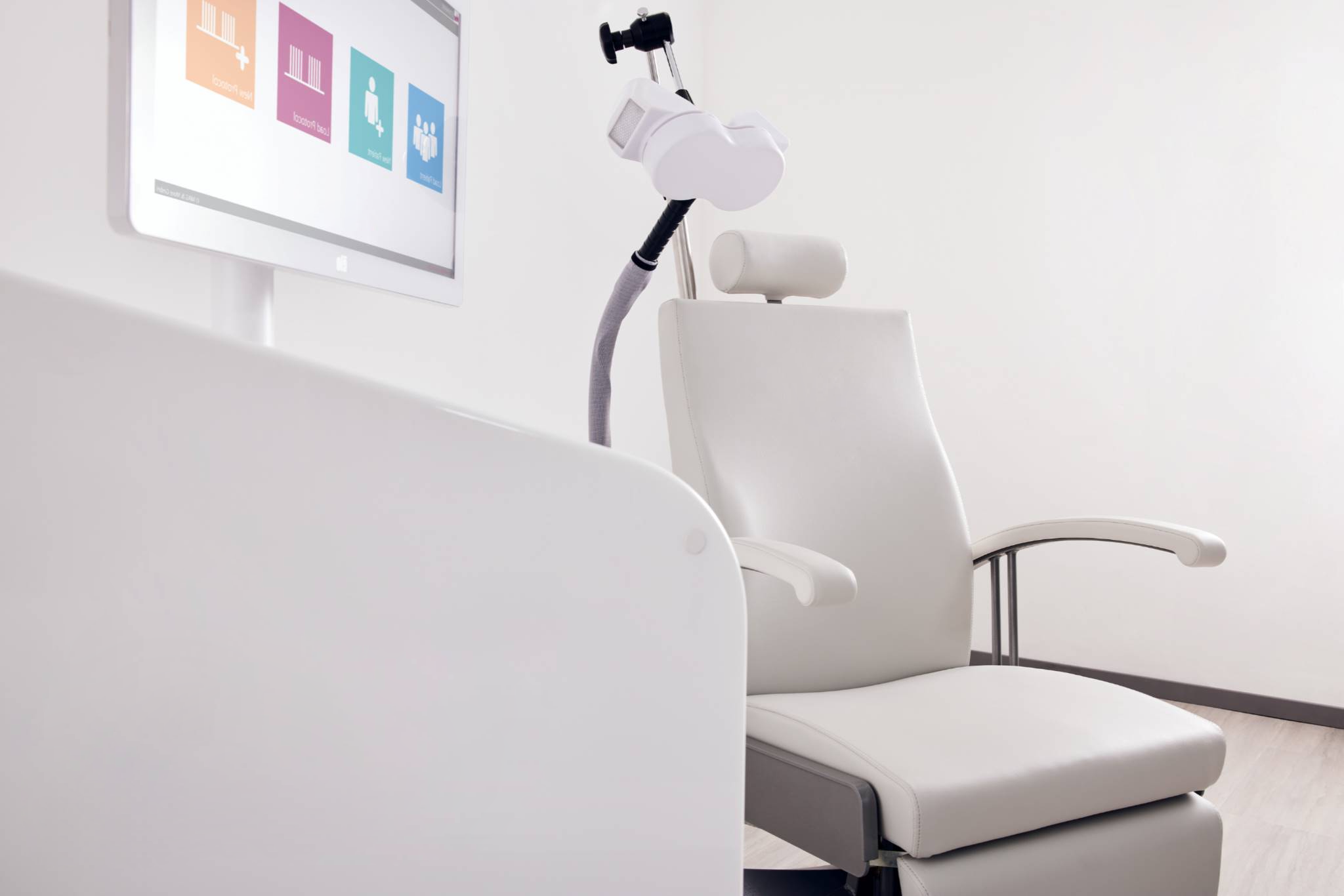
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive neuromodulation technique that uses powerful magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Because there is no surgery or anaesthesia, it has become a safe, well-tolerated option for both research and therapy.
How Does TMS Work?
TMS operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction. During a session an electromagnetic coil is placed near the scalp and delivers magnetic pulses. These pulses pass through the skull and induce electrical currents within targeted neurons. Depending on the pulse frequency, intensity and duration, TMS can either enhance or inhibit neuronal activity.
Applications of TMS
- Research and mapping brain function: By stimulating specific regions and observing behavioural changes, neuroscientists can better understand cognition, language, memory and perception.
- Treatment of depression: Repetitive TMS (rTMS) is approved in several countries as a treatment for people whose depression has not responded to other therapies. It targets mood-regulation areas such as the prefrontal cortex.
- Other mental health conditions: Trials are underway for anxiety disorders, OCD, PTSD and schizophrenia.
- Pain management: Targeted stimulation can relieve chronic pain conditions including migraines and fibromyalgia.
- Neurorehabilitation: Researchers are exploring TMS for stroke recovery and traumatic brain injury rehabilitation.
TMS represents an exciting frontier in neuroscience and mental health. Its ability to modulate brain activity safely and precisely is opening new therapeutic possibilities for people across Perth.